06.25.19 By Anuja Mandke

As the marketplace gets more competitive, the pressure to excel in providing innovative digital experiences in every software and product release is paramount. To remain competitive, organizations are doing whatever they can to push their products to the market before their competition does. Because of this urgency, development and testing cycles are being squeezed. Delivery teams need to innovate and augment their development and testing methods with the adoption of next-generation test automation and continuous testing processes to accelerate releases while still keeping an eye on quality.
Continuous Testing (CT), is the repetitive process of testing in a continuous manner to deliver superior quality applications and software. This process is part of the SDLC (Software Development Lifecycle) and begins during the creation of the initial level of development plan through the release of the final product. Continuous testing facilitates the rapid feedback of any bugs or risks associated with the release/module/product that is being developed or upgraded. This process involves the execution of automated tests as a part of the software delivery pipeline which runs separately from unit tests.
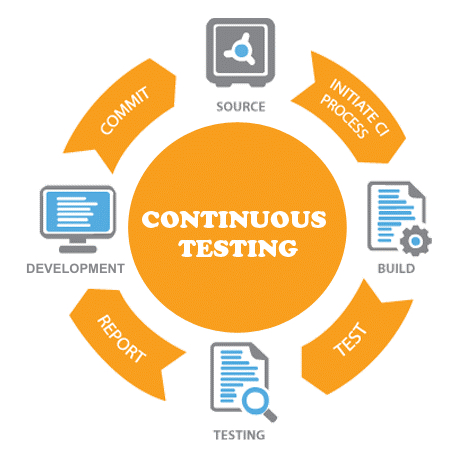 This image* shows a continuous delivery cycle, involving development, source commit, deployment and monitoring. This process, as depicted in the image, allows the commitment of new code modules as they are ready, enabling the development team to quickly push updated code for testing. The code then triggers a Continuous Integration (CI) process which deploys the code into the target environment, initiating a set of automated tests to analyze if the newly committed code is impacting any existing functionality. The results of these tests are then passed on to the development team to decide next steps. Continuous testing can create immense value for businesses through a high level of integration and automation of testing and deployment.
This image* shows a continuous delivery cycle, involving development, source commit, deployment and monitoring. This process, as depicted in the image, allows the commitment of new code modules as they are ready, enabling the development team to quickly push updated code for testing. The code then triggers a Continuous Integration (CI) process which deploys the code into the target environment, initiating a set of automated tests to analyze if the newly committed code is impacting any existing functionality. The results of these tests are then passed on to the development team to decide next steps. Continuous testing can create immense value for businesses through a high level of integration and automation of testing and deployment.
Out of the 5 aspects mentioned above, the cost of poor-quality hurts organizations the most, as can be seen in a recent report* from CISQ (Consortium for IT Software Quality). The cost of poor-quality software in the US in 2018 was approximately $2.84 trillion, and close to 17% of that cost was the time and effort required to find and fix defects.
The report also cites some of the recent examples of how software failures have impacted brands:
There are numerous instances across industries including states, banks, and health services etc. suffering losses due to software failures, most of which could have been detected and addressed or avoided through better software quality assurance processes.
Conclusion:
Continuous testing (CT) enables cost-effective and rapid releases by detecting issues early in the development cycle to optimize development and reduce overall project costs. With CT, software delivery becomes more agile with improved quality and faster product releases. Contact us if you would like to explore how CT can help you expedite your application release cycle.