This blog explores the process and benefits of migrating an on-premise transportation management system (TMS) to the cloud. Learn how a cloud-based TMS will help you manage the peak shipping season better and faster.
According to Adobe Analytics, the 2021 holiday season has already brought in over $109.8 billion in sales. At the peak of Cyber Monday, consumers spent $12 million every minute.
It is safe to say that peak season lives up to its name.
The Transportation and Logistics (T&L) market in the United States is a significant and dynamic industry. It encompasses various modes of transportation, including trucking, rail, air cargo, maritime shipping, and pipelines. The rise of e-commerce has had a profound impact, driving increased demand for last-mile delivery services and specialized logistics solutions. Technological advancements, such as automation, data analytics, and digital platforms, are enhancing efficiency and transforming operations. The competitive landscape is diverse, with large multinational corporations, regional players, and specialized providers. Also, the T&L market in the US is constantly evolving, influenced by economic factors, and changing consumer preferences.
According to a report by Grand View Research, the global logistics market size was valued at USD 6.1 trillion in 2020 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.5% from 2021 to 2028.
The Role of TMS in T&L
A Transportation Management System (TMS) is a vital tool for Transportation & Logistics companies, enabling efficient management of transportation for multiple clients, better carrier negotiations, and real-time visibility for clients. By leveraging a TMS, 3PLs can provide cost-effective and reliable transportation solutions, ensuring competitiveness in the market. The TMS enhances operational efficiency, reduces costs, improves customer service, ensures compliance, supports data-driven decision-making, fosters carrier collaboration, and offers scalability and flexibility. It streamlines operations and optimizes transportation processes, leading to increased productivity and improved overall supply chain performance in T&L.
The global market for Freight Management Systems is estimated at $10.8 Billion, and the US is estimated at $3.8 Billion in 2022. – Research & Markets
Seasonality in Transportation and Logistics
The T&L industry experiences seasonal shifts in market conditions that impact rates and capacity. It typically observes four seasons. The Quiet Season falls in between January to March. It sees a slow recovery after the holidays and increasing freight volume as spring approaches. The Produce Season spans from April to July and brings a surge in freight volume due to the active produce market, resulting in higher rates and increased competition for carriers. The Peak Season occurs from August to October. Heightened shipping activities characterize it as companies prepare for holidays and back-to-school season, leading to peak freight volume and rates. Finally, the Holiday Season in November and December experiences a rush in shipping as shippers aim to complete orders before closures, making it the busiest time for last-minute shipments.
The seasonality in T&L impacts and demands changes in technology. Let us understand how.
Workload Patterns and their impact on TMS
In software systems, workload patterns refer to the characteristics and variations of the tasks and requests the system handles. These patterns help us understand the nature of the workload and the design of software architecture and infrastructure, leading to effective handling of demands. Understanding the workload patterns helps software architects and system administrators design scalable and resilient systems that can handle varying demand levels efficiently. Here are some of the most common workload patterns:
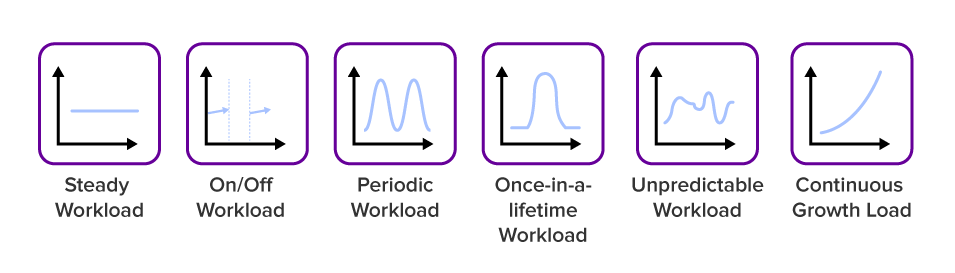
- Steady Load: This pattern represents a consistent and stable workload over time. The system experiences a relatively constant level of requests and tasks without significant fluctuations.
- On/Off Load: This pattern alternate between periods of low demand and sudden bursts of demand. These bursts are intermittent and can happen unpredictably. Systems need to be capable of quickly scaling up to accommodate the spikes and then scale down when the bursts subside.
- Periodic Load: Periodic load patterns involve regular and predictable fluctuations in workload based on specific seasons or recurring events. Industries like retail, travel, or hospitality may experience varying levels of demand based on holidays, vacations, or other seasonal factors.
- Once-in-a-lifetime Load: Once in life time load occurs when the system experiences a sudden surge in demand, typically during specific periods or events. For example, tax filing platforms may experience high traffic and transaction volumes during March/April time.
- Unpredictable Load: Unpredictable load patterns involve sudden and temporary spikes in workload, typically caused by unpredictable events or conditions. For example, a news website may experience a burst load when breaking news occurs, resulting in a surge of visitors seeking real-time updates.
- Continuous Growth Load: This pattern involves a gradual and constant increase in workload over time as the system’s user base or data volume grows. It may be driven by business expansion, user acquisition, or increasing data processing requirements.
The T&L industry falls under the periodic workload pattern due to the seasonality in the business. To keep the business running at optimal performance, T&L companies must ensure the provision of infrastructure and relevant resources at the peak level. To do so, organizations spend more CAPEX, and the extra capacity remains idle during non-peak seasons, leading to cost over heads and maintenance.
Handling periodic workloads in on-premise systems significantly impact resource planning, scalability, infrastructure provisioning, performance optimization, redundancy, high availability, cost considerations, and flexibility. These workloads require careful resource planning to ensure sufficient capacity during peak periods, which may involve scaling hardware resources and optimizing system configurations. Provisioning the right resources is crucial to handle workload spikes effectively and maintain optimal performance. Redundancy and high availability measures are essential to minimize downtime and ensure continuous operation. However, cost considerations should be weighed since resource allocation may lead to underutilization during off-peak periods, increasing operational costs. The flexibility and adaptability of on-premise systems are vital in accommodating changing workload patterns, allowing for dynamic resource scaling and efficient resource allocation. Assessing the trade-offs and considering hybrid cloud or cloud-based solutions for added scalability and cost optimization is essential.
Cloud to the rescue
The evolution of cloud computing has revolutionized the way organizations handle their IT infrastructure and operations. Initially, cloud technology offered on-demand access to computing resources, storage, and applications, enabling businesses to reduce capital expenses and pay for services as needed. Over time, cloud platforms evolved to provide greater flexibility, scalability, and security, allowing organizations to easily scale their operations to meet changing demands. By leveraging cloud services, organizations can quickly deploy and scale resources, whether it’s expanding server capacity, handling higher website traffic, or accommodating spikes in data storage. Cloud computing also fosters collaboration, enhances data accessibility, and facilitates remote work, enabling organizations to adapt rapidly to market shifts and improve overall efficiency.
The global market for Digital Transformation Spending in Logistics, estimated at US$52.3 Billion in the year 2022, is projected to reach a revised size of US$108.8 Billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 9.6%. – Research & Markets
Here’s how migrating to the cloud can simplify managing periodic workloads compared to on-premise systems:
- Scalability: Cloud platforms offer elastic scalability, allowing organizations to scale resources up or down based on workload demands. Additional computing power and storage can be provisioned during peak periods, ensuring optimal performance and handling increased demand. Conversely, resources can be scaled back during off-peak periods to avoid unnecessary costs.
- Cost Optimization: Cloud services operate on a pay-as-you-go model, enabling organizations to only pay for the resources they use. This feature eliminates the need to provision and maintain excess hardware resources to handle periodic peaks, resulting in cost savings. The ability to scale resources dynamically also ensures efficient resource utilization, reducing overall operational costs.
- High Availability: Cloud providers offer built-in redundancy and high availability features. Organizations can ensure continuous operations during peak periods by leveraging multiple data centers and regions. Redundancy, automatic failover, and data replication mechanisms provided by cloud platforms minimize the risk of downtime and ensure business continuity.
- Flexibility and Agility: Cloud-based systems provide greater flexibility and agility than on-premise solutions. Scaling resources, deploying new instances, and adapting to changing workload patterns can be done quickly and efficiently. Organizations can respond effectively to workload fluctuations, ensuring optimal performance and user experience.
- Managed Services: Cloud providers offer a wide range of managed services, such as auto-scaling, load balancing, and database management. These services simplify the management and optimization of workload patterns, offloading some operational burdens from organizations and allowing them to focus on their core business activities.
- Global Reach: Cloud platforms have a global presence with data centers in multiple regions. The broad reach enables organizations to leverage the cloud’s proximity to end-users, reducing latency and improving the user experience during peak periods. It also facilitates the seamless expansion of operations across different geographical locations.
- Continuous Innovation: Cloud providers invest heavily in Research and Development, continually introducing new features, services, and performance improvements. By migrating to the cloud, organizations can leverage these innovations and stay ahead in managing periodic workloads effectively.
Migrating on-premises applications to the cloud empowers organizations to efficiently manage periodic workloads, improve performance, and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
The worldwide end-user spending on public cloud services is forecasted to grow 20.7% to $591.8 billion in 2023, up from $490.3 billion in 2022, higher than the 18.8% growth forecast for 2022. – Gartner Inc
Let us look at the steps involved in migrating an on-premise system to the cloud.
Cloud Migration Strategy
Cloud migration strategy refers to organizational plan and approach while transitioning their applications, data, and infrastructure from on-premise systems to cloud environments. While specific strategies may vary depending on the organization’s goals and requirements, a typical cloud migration strategy involves the following key steps:
- Assessment and Planning: This phase involves assessing the existing infrastructure, applications, and data to determine the feasibility and benefits of migrating to the cloud. It includes identifying the systems to be migrated, understanding dependencies, conducting cost analysis, and setting migration goals.
- Application and Data Analysis: Organizations must evaluate their applications and data to determine cloud compatibility. This phase involves categorizing applications based on their characteristics (e.g., mission-critical, legacy, or cloud-native), identifying potential modifications or rearchitecting needs, and analyzing data storage and migration requirements.
- Cloud Provider and Architecture Selection: Organizations must select the most suitable cloud provider(s) to fulfill specific needs, such as performance, security, compliance, scalability, and cost. They also need to design an architecture that follows best practices and leverages all capabilities of the chosen cloud provider.
- Migration Approach: There are several migration approaches to consider, such as the “lift and shift” method (rehosting applications as-is in the cloud), rearchitecting applications to take advantage of cloud-native features, or rebuilding applications entirely. The selected approach will depend on application complexity, time constraints, and cost considerations.
- Data Migration: Organizations need to plan and execute the migration of their data to the cloud, ensuring data integrity, security, and minimal downtime. Depending on the volume and sensitivity, strategies may include offline data transfer, incremental sync, or real-time replication.
- Testing and Validation: Thorough testing and validation are vital to ensure the migrated applications and data function well in the cloud environment. This step involves performance, functional, security, and user acceptance testing to verify that the applications meet the expected requirements.
- Deployment and Cut-Over: Once testing is complete, the deployment and cut-over phase involves transitioning from the on-premise environment to the cloud environment. This movement may include redirecting traffic, updating DNS settings, and finalizing configuration for the cloud environment.
- Post-Migration Optimization: After migration, organizations should optimize their cloud resources, fine-tune configurations, and optimize costs based on usage patterns. Ongoing monitoring, performance optimization, and security management are crucial to this strategy.
It’s important to note that the cloud migration strategy aligns with the organization’s unique needs and includes additional steps based on specific requirements. It should also have a robust change management and communication plan to ensure smooth adoption and minimal disruption to business operations.
Emtec Digital: Your Reliable Cloud Partner
At Emtec Digital, we help organizations achieve digital maturity by migrating on-premise applications to a combination of public, private, and hybrid clouds. Our experts help fulfill desired business goals by deploying technical services using the following step-by-step process:
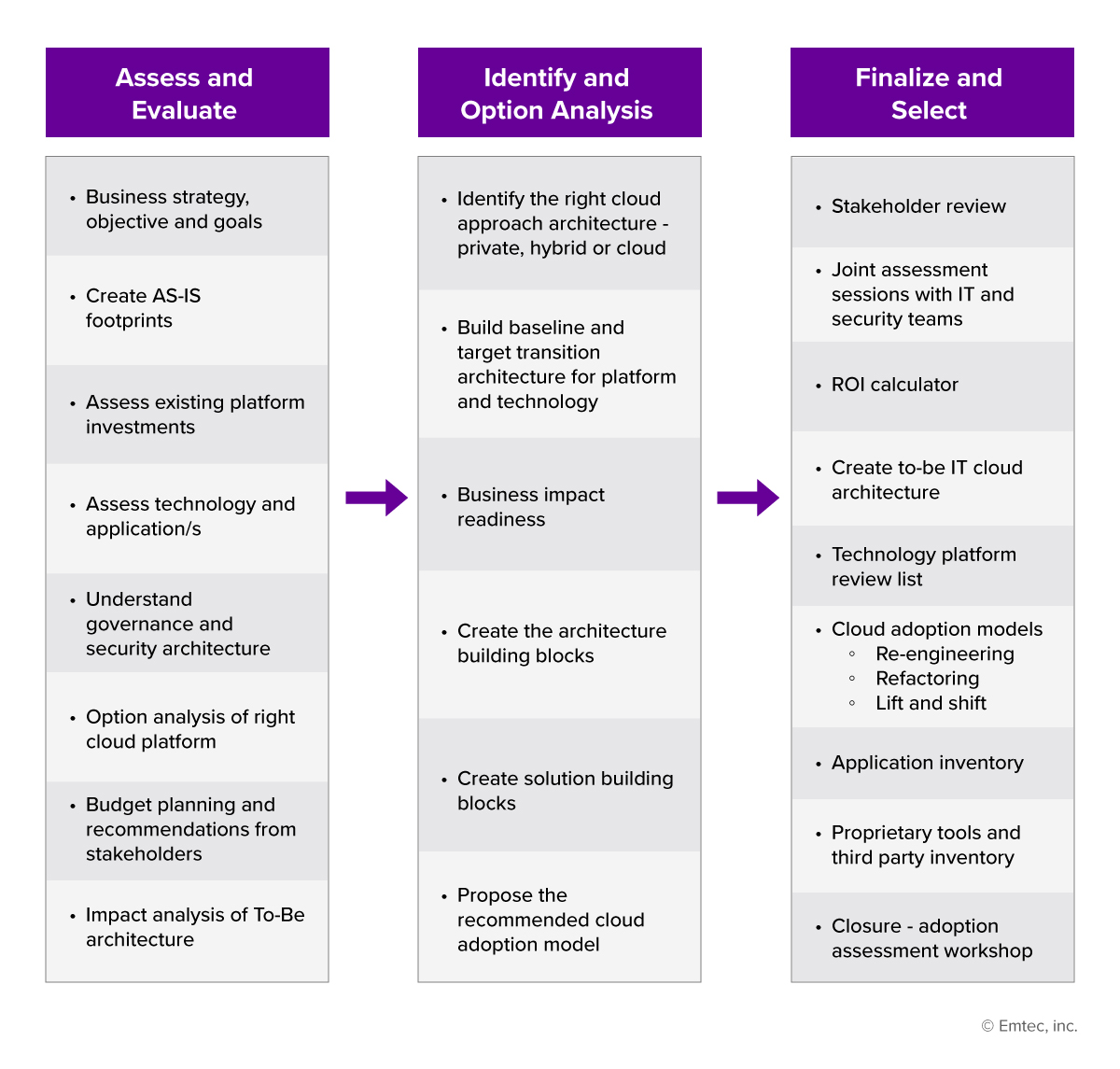
Our experts will hold your hand for a seamless migration and integration of your TMS, from technology consultation to transition and post-migration support. Leveraging a winning process, we will help you overcome all your technical inhibitions and instill confidence to adopt upcoming technology.
Want to leverage the power of a cloud-based TMS to meet peak demands?
References
blog.adobe.com/en/publish/2021/11/30/adobe-consumers-spent-10-8-billion-on-cyber-monday-109-8-billion-so-far-this-holiday-season
www.researchandmarkets.com/report/freight-management-system
www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2022-10-31-gartner-forecasts-worldwide-public-cloud-end-user-spending-to-reach-nearly-600-billion-in-2023



